China Manufacturer High Quality Slewing Ring Bearing
How to correctly install and maintain the slewing ring bearing
The following describes the correct installation and maintenance methods for the slewing bearing (slewing bearing) from three aspects: transportation, storage, installation and maintenance:
I. Transportation and storage of slewing ring bearing
The slewing bearing (slewing ring bearing) has been coated with anti-rust oil before leaving the factory and wrapped with film and linen. The rust-proof period of this package is generally 3-6 months.
The storage temperature should be 20±10°C, and the relative humidity is not more than 60%. After the expiration date, it should be maintained in time. The slewing bearing stock should be filled with grease after one year and check the flexibility of its rotation.
The slewing ring bearing (slewing bearing) is usually fixed on the pallet or in the package when it leaves the factory. It is available in single-piece packaging and group packaging.
Transportation and storage should be kept level, can not be collided and squeezed, can not be rained, and the storage should be flat. There should be a flat separation between the stacked slewing bearings. The slewing ring bearing generally has a lifting hole, which can be screwed into the eyebolt for safe lifting.

Second, the installation of slewing ring bearing
First open the slewing ring bearing (slewing bearing) package, check the certificate and the sign, and confirm that the slewing bearing type used is correct. The installation steps are as follows:
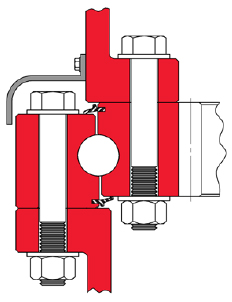
A, the installation plane of slewing ring bearing
The mounting surface should be smooth and remove all excess material such as paint residue, solder beads, burrs, etc. When cleaning, be careful not to let the solvent penetrate into the inside of the slewing ring, and do not use solvents that damage the sealing material.
The mounting surface should be dry and free of lubricant before assembly. Measures to protect workers and the environment should be taken.
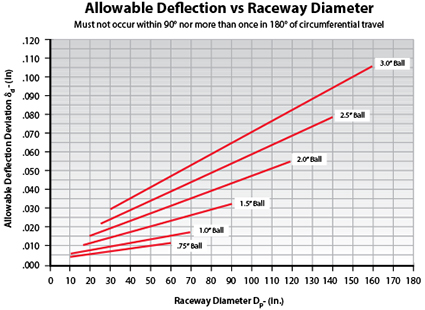
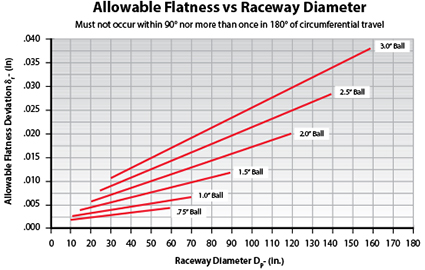
B, the rigidity of the support
Standard slewing bearings and zero-gap slewing bearings have different requirements for the rigidity of the bearings.
C, positioning of slewing ring bearing
The inner and outer ring raceways of the slewing ring have a soft belt and should be placed on both sides of the main load plane. That is, it is shifted by 90 degrees from the main load zone.
There is a blockage at the soft belt or an “S” mark. Also check the slewing bearing and the mounting surface, usually with a feeler gauge. If the fit is not good, fill it with a suitable material. Welding work on the support is prohibited after installation of the slewing ring bearing.
D, solid bolt
1, the choice of mounting bolts
The bolts and washers should be installed using the specified (size, quantity, strength rating, etc.). Also note: Do not use fully threaded bolts, do not use old bolts, nuts and washers, do not use open washers such as spring washers, etc.
2, the choice of bolt pre-tightening torque
The pre-tightening force of ordinary metric bolts is recommended to take 0.6-0.7 times the bolt yield strength. It is recommended that the bolts larger than M27 use hydraulic fastening devices, and the pre-tightening force should not exceed 85% of the yield strength.
3, fastening bolts
The slewing ring should be installed under no load conditions. Note: Apply a little oil to the thread of the bolt to ensure that the friction resistance is balanced. Do not use glue on the bolt lock. Pre-tightening bolts: The pre-tightening should be carried out in three steps. The three-step force is 30%, 80%, and 100%, respectively.
E, adjust the gear backlash of slewing ring bearing
When installing a toothed slewing ring, it is important to properly adjust the gear backlash. It can be measured with a feeler gauge at the highest point of the radial runout of the gear, or it can be pressed with lead wire or other suitable method. If the backlash is not within the specified value, the movable pinion changes the center distance.
After setting, turn the slewing ring at least one full turn to confirm that there are no other tooth high jump points, and check the backlash false back gap after the slewing bearing is finally fixed. The highest point of the radial runout of the gear is marked in the groove with green paint.
F, first lubrication
1. Raceway lubrication To ensure sufficient lubrication, the grease specified in the drawings or the product manual should be refilled before initial use. Pay special attention to all the grease nozzles injecting the grease one by one, preferably by turning the slewing bearing while filling the oil until the grease is squeezed out of the seal.
2. Gear lubrication When the gear is lubricated, the tooth surface should be clean. It is recommended to brush the grease on the gear with a clean brush.
Third, regular inspection and maintenance of slewing ring bearing
Check the bolt preload torque for the first time using 100 working hours. If more than 10% of the bolts are loose, check again after the 200th working hour.
It will be inspected every 500 working hours in the future; the inspection interval should be shortened in harsh conditions.
After 2000 hours of cumulative operation of the equipment, if a bolt is found to be loose to less than 80% of the specified torque, the bolt and the adjacent two bolts are replaced. If 20% of the bolts are found to be loose to less than 80% of the specified torque, all bolts will be replaced.
After the equipment has been working for 14,000 hours, all the bolts will be replaced.
For equipment with a high speed of rotation or continuous rotation or frequent operation, add oil every 100 working hours. In the case of poor working conditions, the time interval for filling grease should be further shortened.

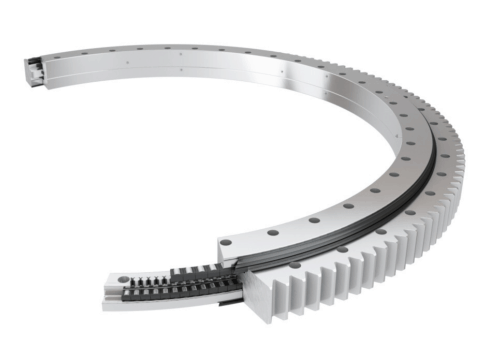 Slewing ring bearings, or turntable bearings, are ball or roller style bearings composed of two concentric rings either of which may include a gear. This type of bearing enhances load support and power transmission in all directions, and is typically employed to support heavy loads for slow applications and large equipment such as earth excavators and construction cranes. The unique power and versatility of slewing ring bearings has made them increasingly valuable in a wide array of industries, including construction, industrial, robotics, machine tooling, and medical applications.
Slewing ring bearings, or turntable bearings, are ball or roller style bearings composed of two concentric rings either of which may include a gear. This type of bearing enhances load support and power transmission in all directions, and is typically employed to support heavy loads for slow applications and large equipment such as earth excavators and construction cranes. The unique power and versatility of slewing ring bearings has made them increasingly valuable in a wide array of industries, including construction, industrial, robotics, machine tooling, and medical applications.